Sustainability and Financial Performance
Business Processes enabling Impact Goals
Mathias Kirchmer, Scheer Americas and Widener University, Afrooz Moatari-Kazerouni and Yvonne Lederer Antonucci, Widener University
(Titelbild: © AdobeStock | 520479433 | Cagkan)
In Short
This paper outlines key considerations for organizations looking to align financial performance and sustainability through their business process management practices. By adopting these considerations, businesses can achieve long-term benefits for both financial performance and sustainability and become more socially responsible and environmentally sustainable.
Business process management (BPM) aligns financial and social goals. It designs and controls business processes. Green BPM integrates sustainability, promoting ESG principles. Benefits include brand value and access to capital. Challenges are ESG complexity and integration costs. Sustainable processes improve financial performance and mitigate conflicting goals.
1. Importance of Combining Sustainability and Financial Performance through BPM
In today’s markets, organizations are not only under pressure to deliver strong financial performance but also to be socially responsible and environmentally sustainable. With global concerns for climate change, resourced depletion, and social inequality becoming more pressing in recent years [1, 2], the ability to integrate sustainability capabilities within business processes has gained significant attention among organizations. The business process management (BPM) discipline is critical for aligning financial performance and sustainability due to its systematic approach to designing, implementing, executing, and controlling business processes [3, 4]. It moves the integrated business strategy into people and technology-based execution, at pace with certainty [4, 7]. It is an effective way to reduce environmental impact, promote social justice, and ensure long-term viability. BPM promises to improve performance through a radical, top-down enforced change based on a process-oriented rethinking of an organization [5, 6, 7]. By adopting this strategic and proactive approach, businesses can integrate sustainability into their processes and achieve long-term benefits for both financial performance and sustainability. However, business processes must be designed to incorporate and support these two objectives. Furthermore, organizations should follow a strategic approach with appropriate process governance to manage the complex tradeoffs that may arise [7, 8].
2. Sustainability through BPM
Sustainability is the organization’s ability to demonstrate and maintain positive economic, social, and environmental performance over the long term [9, 10]. The concept of sustainability has introduced environmental considerations into economic sciences [11]. Elkington [12], in The Triple Bottom Line book, distinguished three dimensions of sustainability, i.e., economic, social, and environmental. These dimensions are the basis of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance), today’s most widely accepted measure of organizational sustainability and social impact [13]. ESG is a valuable tool for companies to position themselves as socially responsible businesses and enhance economic performance. Sustainability through business processes promotes the integration of these practices into the core operations of a business. Also referred to as Green BPM, it is the set of management activities that help to monitor and reduce the environmental impact of business processes in their design, implementation, execution, and control stages, as well as leading to cultural change within the process life cycle [14]. When embedded into the organizational vision through the discipline of process management, the “strategic management green view” results in implementing environmentally responsible practices, social responsibility initiatives, and governance practices that foster transparency and accountability in decision-making [7, 14].
It has become increasingly essential for organizations aiming to align their business practices with sustainability goals in order to realize their overall business strategy. Moreover, achieving sustainable green transformation and economic growth is linked to organizations‘ innovation ability [4, 15]. By adopting process management capabilities, innovation would promote analyzing and optimizing processes to improve efficiency and reduce waste, creating a practical approach to enhancing ESG performance. ESG measures can guide BPM efforts by providing a framework for incorporating sustainability and ethical considerations into business operations. In this regard, BPM can help organizations identify opportunities to enhance their social impact, such as improving working conditions or supporting local communities.
Benefits and Challenges of Integrating ESG and Sustainability in Business Processes
Integrating ESG principles into an organization’s business processes requires a holistic approach involving all aspects of the business [16], including sales, production planning, supply chain management, product design and production, quality assurance, and maintenance processes. Implementing ESG through these business aspects can serve several advantages, including enhanced reputation and brand value, improved risk management, increased operational efficiency, and access to new markets and customers who value sustainability. In addition, organizations that prioritize ESG measures, e.g., through BPM, may be seen as less risky investments by investors, leading to increased access to capital [17].
However, there are challenges associated with integrating ESG measures into business processes. ESG measures are often complex and can be difficult to quantify. Within ESG integration, managers employ various methods and strategies, competing against managers that do not bear the costs of ESG integration [18]. In addition, implementing changes to business processes can be time-consuming and expensive and may require significant investment in technology and training.
Despite these challenges, integrating ESG principles into business processes is becoming increasingly important for companies that want to remain competitive and meet the demands of investors and consumers. BPM has become the management discipline that helps make this happen through appropriate process lifecycle management, creating transparency [14] and addressing all business process components, e.g., organization, data, functions, deliverables, and control [4, 19].
Sustainability Indicators and Reporting
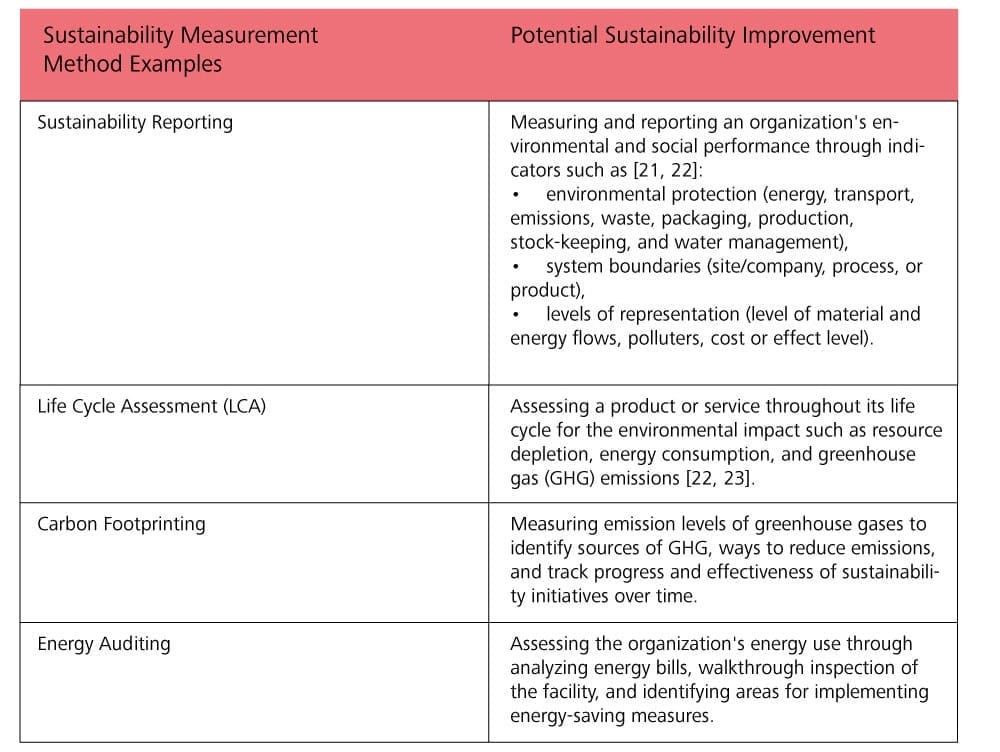
Measuring sustainability as part of appropriate process governance is essential for businesses to minimize their environmental impact and ensure long-term viability. Various methods and tools measure and improve sustainability, as listed in Table 1. BPM Tools, such as process mining, analytics, and process modeling, support the measurement and governance of processes and the application of sustainability methods [20].
By implementing these methods and leveraging BPM, businesses can reduce their environmental impact and improve their bottom line while demonstrating their commitment to sustainability to their stakeholders. ESG measures assess the effectiveness of BPM initiatives. By tracking ESG performance over time, organizations can evaluate the impact of process improvements on sustainability and ethical practices. This results in identifying areas for further improvement and demonstrating their commitment to ESG goals to stakeholders.
3. Financial Performance of Sustainable Processes through BPM
With sustainability becoming an increasingly important concept in business, many organizations have adopted sustainable business processes to reduce their environmental impact and promote social responsibility while enhancing their financial performance. These organizations must embrace a strategic and proactive approach to BPM to achieve this integration of sustainability and financial performance.
BPM provides the transparency necessary to achieve financial performance results and mitigate the tradeoffs of conflicting goals, such as efficiency and compliance or agility and standardization [8], required for financial performance. BPM provides visibility into the organization to take fast but well-informed decisions and launch appropriate actions. It creates the foundation for effective digital transformation [24, 25].
Combining Sustainability and Financial Performance
The integration of ESG criteria in an organization’s operations has been linked to improved financial performance, making it a crucial component of BPM. The consideration of specific ESG components is essential to understanding the impact of ESG criteria on financial performance for business processes. „Environmental“ refers to the organization’s impact on the natural environment, including resource consumption, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions. “Social“ relates to the organization’s impact on its stakeholders. „Governance“ refers to the organization’s management and oversight practices, including board diversity, executive compensation, and shareholder rights [26].
These three components cover a broad spectrum of issues that traditionally were not part of financial or economic analysis but are significant in financial decision-making. Today, ESG performance is directly linked to financial performance, where a quarter of global assets are managed under Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) [27]. ESG is related to improved Return on Equity (ROE), Return on Assets (ROA), stock price, operational efficiency, and risk management [28]. Studies have shown that businesses embracing sustainability tend to financially outperform those not in the long term [28-31].
The belief is that organizations oriented towards ESG achieve better growth, cost savings, profitability, strengthening of stakeholder relations, and improving their brand and reputation. The last two are key parameters for an organization’s sustained performance and long-term prosperity [32]. Businesses must adopt a proactive approach to sustainability to align financial performance and sustainability through business processes, thus signifying the formulation of sustainability as a core value of the organization and integrating it into all aspects of the business processes.
Measuring Financial Performance Indicators of Sustainable Processes
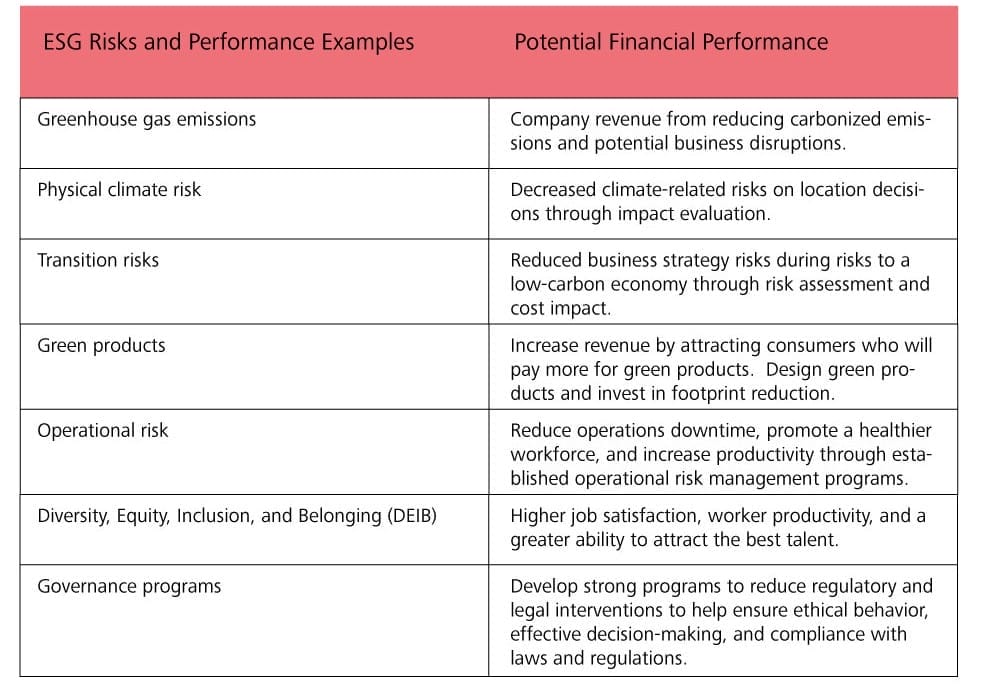
Financial improvements in sustainable processes are ensured when ESG data is collected and reported, and ESG risks are managed. Montenegro [33] identified examples of how ESG risk management and performance improvement can lead to better financial performance (Table 2).
4. Organizational Strategies to Realize Sustainable Processes
Implementing sustainable business processes, and leveraging BPM capabilities, can be a challenging task for organizations. Some of the organizational strategies used to ensure the successful implementation of sustainable business processes include:
- Setting Sustainable Goals and Targets to achieve sustainable business processes by monitoring and evaluating organizational progress toward sustainability.
- Conducting Sustainability Assessments, both internally and externally, to identify their environmental impact, risks, and opportunities for improvement.
- Implementing Sustainable Practices to achieve sustainable business processes by reducing environmental impact and saving costs. Examples of these practices include waste reduction, energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainable procurement.
- Engaging Stakeholders, i.e., employees, customers, suppliers, and investors, to gain support for their sustainability initiatives and generate ideas for improvement.
- Monitoring and Reporting progress towards sustainable business processes to improve, take corrective actions, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability to their stakeholders.
Core Capabilities
Organizations that pioneer sustainable and innovative processes benefit from many first-mover advantages [34], including setting higher prices for their green practices and incorporating social, environmental, and ethical issues into their management decisions. Inspired by prior research [35], the core capabilities of organizations using process management to implement sustainable processes include the following:
- Innovativeness: Organizations with high „green“ innovation intensity can enhance their corporate financial performance through cost leadership and product differentiation.
- Environmental awareness: Organizations that meet environmental and cultural values can develop more advanced and successful environmental management initiatives, while the societies will reward such organizations for their global change progress initiations.
- Adoptability to stringent environmental regulations: Highly stringent environmental regulations force firms to implement advanced environmental management practices and effectively force them to innovate.
5. Predictions and Recommendations
Organizations must integrate sustainability into all aspects of their business processes, addressing the entire process lifecycle: design, implementation, execution, and control. As pressure increases from the United Nations and governments to combine sustainability and financial performance, this alignment becomes mandatory. They need to establish processes that deliver financial performance through appropriate sustainability. The BPM-Discipline and underlying digital process management tools, such as process mining, analytics, and modeling tools, support this objective.
Successful companies view sustainability as a long-term goal by committing to a proactive approach that involves continuous improvement. They establish appropriate process governance that uses the right metrics to measure their sustainability and financial performance. The BPM-Discipline provides the management discipline to move this overall strategy into people and technology-based execution fast and reliably [7].